VPN Hubs
VPN Hubs are the gateway servers that handle VPN tunnel termination and route traffic between connected clients and your internal network. Each hub runs the ThetaSecure Network Connector and registers itself with the platform to receive configuration and report its status.
Navigate to Configuration > VPN Hubs to view and manage your gateway servers.
The sidebar label for this page is "VPN Hubs" while the page title displays "VPN Servers." Both refer to the same set of registered VPN gateway instances.
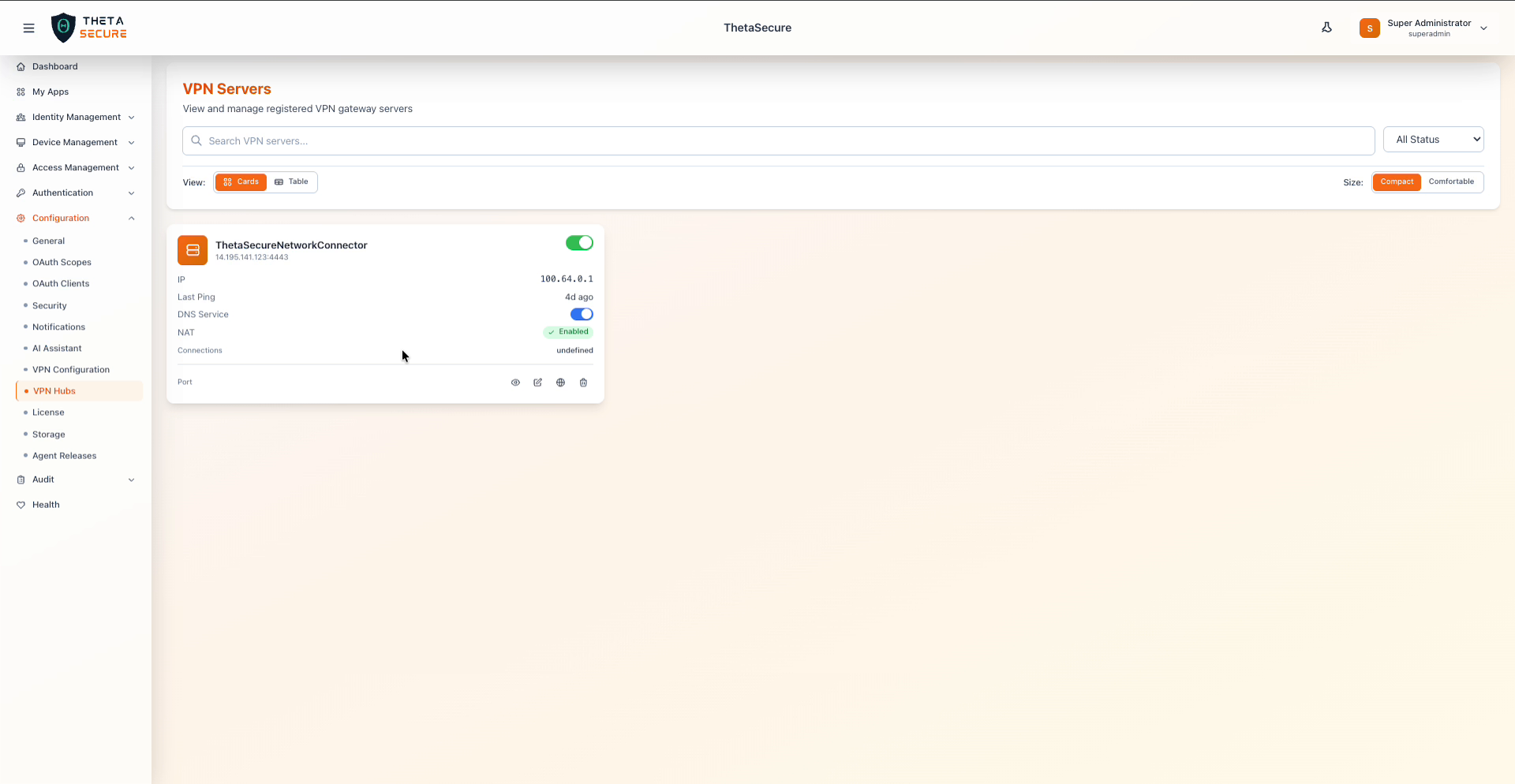 VPN Servers page with a registered ThetaSecureNetworkConnector hub
VPN Servers page with a registered ThetaSecureNetworkConnector hub
Server List
The server list displays all registered VPN gateway servers. Use the search bar to filter by name. Toggle between Cards and Table views, and adjust the display density with the Compact or Comfortable size options. The All Status dropdown filters by server status.
Server Card
Each server card shows a summary of the hub's current state.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Server Name | The registered name of the VPN hub instance (for example, ThetaSecureNetworkConnector). |
| Address | The public IP address and port the hub listens on (for example, 14.195.141.123:4443). |
| Enabled | Toggle to enable or disable the hub. Disabled hubs stop accepting new connections. |
| IP | The VPN tunnel IP address allocated to this hub from the IP pool (for example, 100.64.0.1). |
| Last Ping | Time since the hub last reported its health status to the platform. |
| DNS Service | Toggle indicating whether this hub provides DNS forwarding for connected clients. |
| NAT | Whether Network Address Translation is enabled, allowing clients to access external networks through this server. |
| Connections | Number of active VPN client connections on this hub. |
Action icons at the bottom of each card allow you to view details, edit, access network diagnostics, or delete the server.
Server Details
Click the view icon on a server card to open the full details panel.
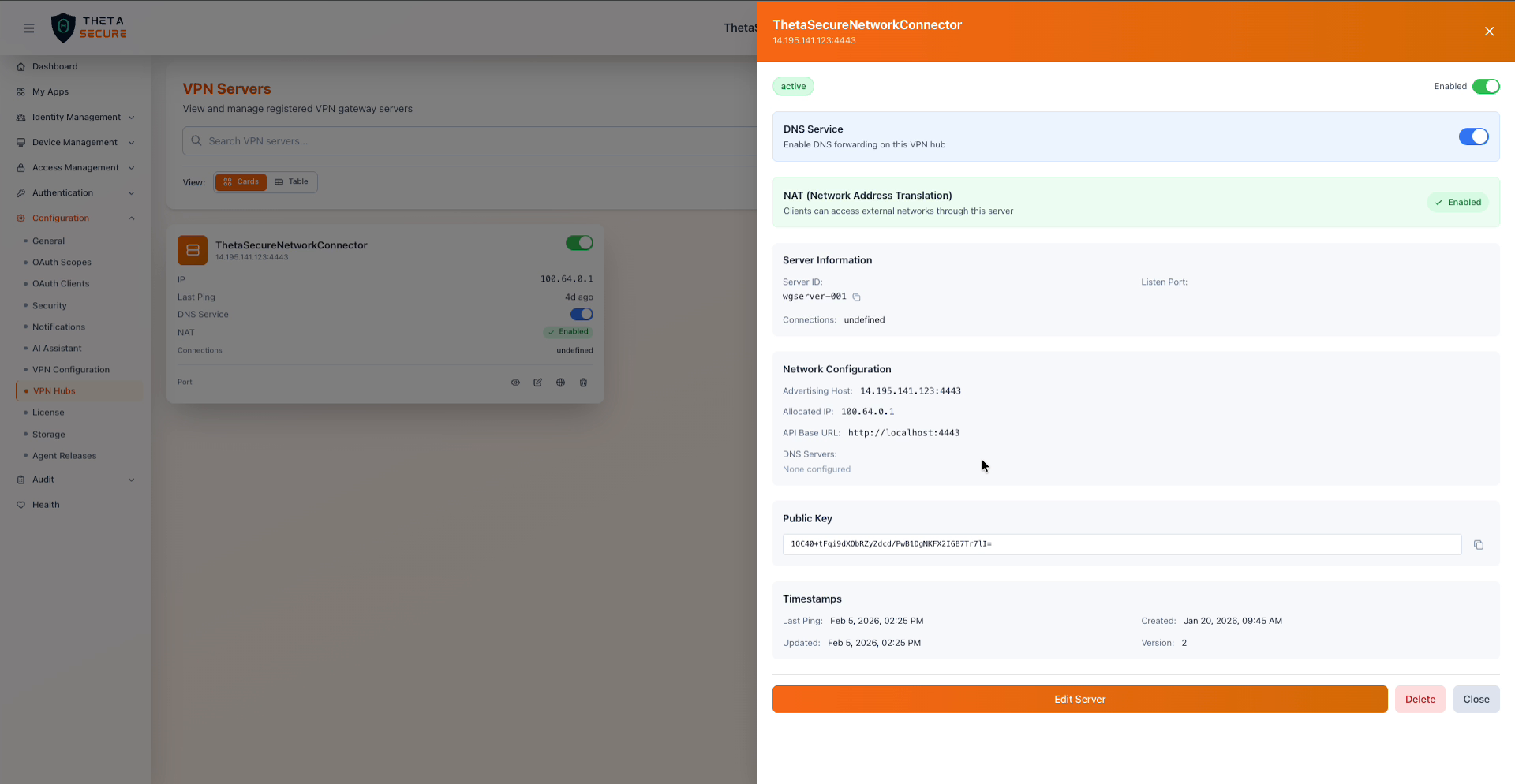 Server details panel with DNS, NAT, network configuration, public key, and timestamps
Server details panel with DNS, NAT, network configuration, public key, and timestamps
Status and Features
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Current registration state of the hub (for example, active). |
| Enabled | Toggle to enable or disable the hub from this panel. |
| DNS Service | Enable DNS forwarding on this VPN hub. When enabled, connected clients can resolve internal DNS names through the hub. |
| NAT (Network Address Translation) | When enabled, clients can access external networks through this server. The panel shows a description confirming that clients can access external networks through this server. |
Server Information
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Server ID | Unique identifier for this gateway instance (for example, wgserver-001). Click the copy icon to copy. |
| Listen Port | The port the WireGuard interface listens on for incoming VPN connections. |
| Connections | Number of active client tunnels on this hub. |
Network Configuration
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Advertising Host | The public address and port that clients use to connect to this hub (for example, 14.195.141.123:4443). |
| Allocated IP | The tunnel IP address assigned to this hub from the VPN IP pool. |
| API Base URL | The local API endpoint the hub uses for management communication (for example, http://localhost:4443). |
| DNS Servers | DNS server addresses configured on this hub for client resolution. Shows "None configured" if not set. |
Public Key
The WireGuard public key for this hub. This key is used by clients to establish encrypted tunnels. The key is generated during hub registration and cannot be changed without re registering the server.
Timestamps
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Last Ping | When the hub last reported its status. |
| Created | When the hub was first registered. |
| Updated | When the hub's configuration was last modified. |
| Version | Configuration version number, incremented with each change. |
Use Edit Server to modify the hub configuration, Delete to unregister the hub, or Close to dismiss the details panel.
Monitor the Last Ping timestamp to detect hubs that have gone offline. A hub that has not reported in for several hours may indicate a network issue, a crashed connector process, or a server that needs to be restarted. Investigate any hub where the last ping exceeds your expected heartbeat interval.