Groups Management
Groups let you organize users into logical collections so you can manage access at scale. Instead of assigning permissions, roles, or applications to individual users, assign them to a group and every member inherits the configuration automatically.
ThetaSecure also ties device binding policies to groups, giving you granular control over which devices are approved for users in each group.
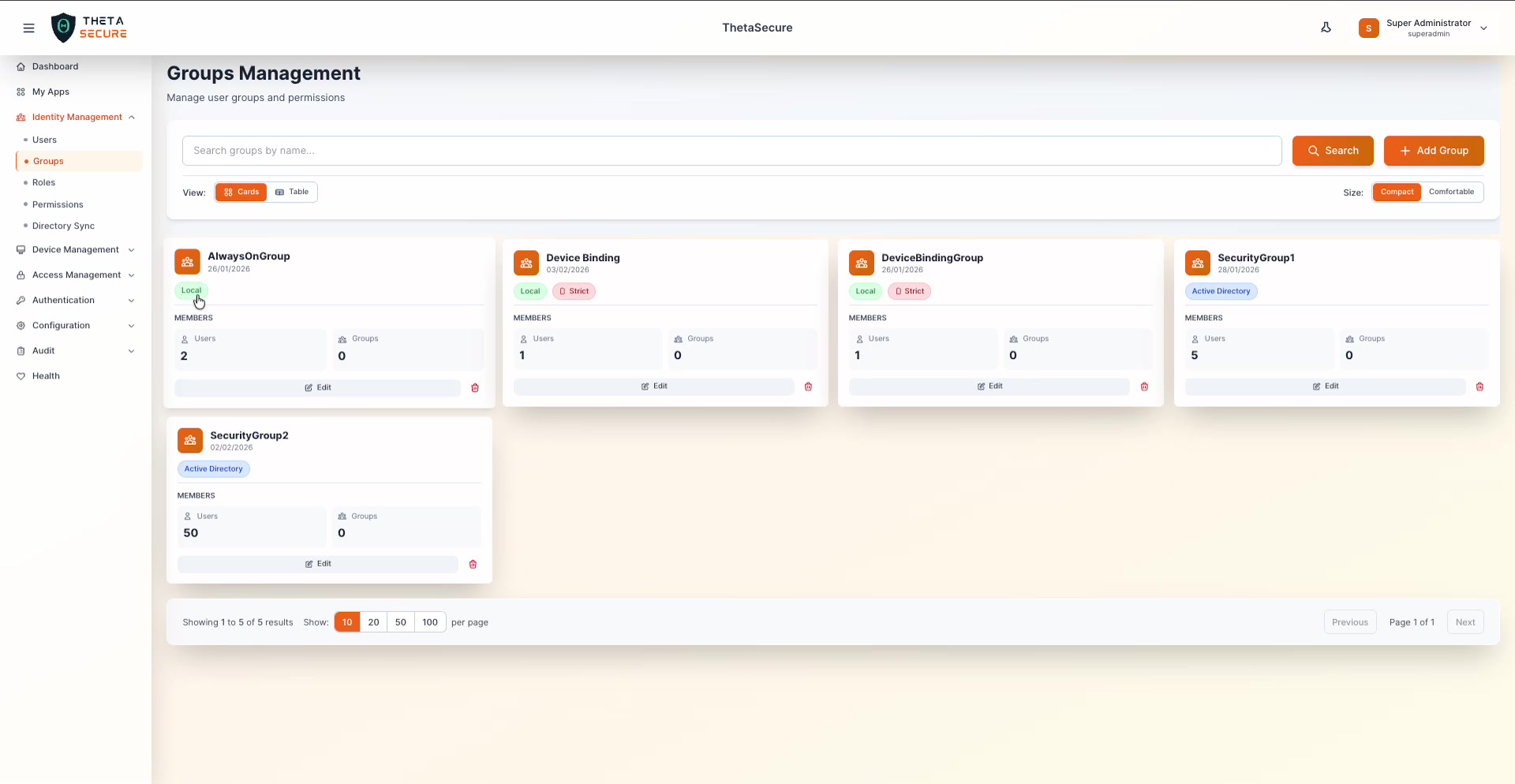
At a Glance
The Groups page shows all configured groups with key details on each card:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Group Name | Display name and creation date |
| Source | Local (created in ThetaSecure) or Active Directory (synced from external directory) |
| Device Binding | Shows the device approval mode if configured (e.g., Strict) |
| Users | Number of user members |
| Groups | Number of nested child groups |
Each card has an Edit button and a Delete (🗑) icon.
View Modes
Switch between Cards (default) and Table view using the toggle in the toolbar.
Table View
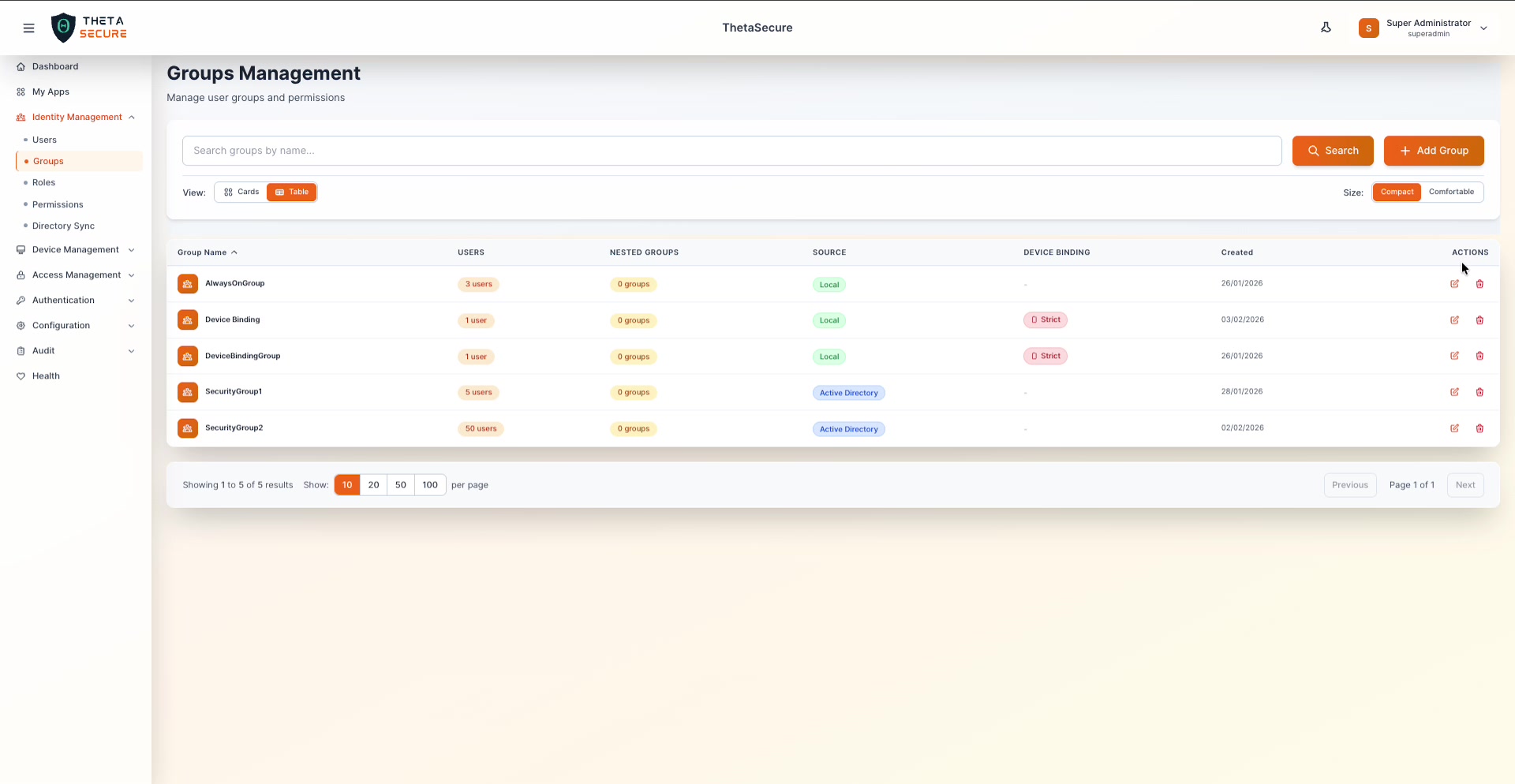
The table view adds sortable columns including Nested Groups, Device Binding status, and Created date. This view is better suited when you have a large number of groups and need to quickly scan device binding configurations or sort by user count.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Group Name | Sortable by name |
| Users | Member count shown as a badge (e.g., "3 users", "50 users") |
| Nested Groups | Number of child groups |
| Source | Local or Active Directory badge |
| Device Binding | Shows mode if configured (e.g., Strict in red) or - if not set |
| Created | Date the group was created |
| Actions | Edit and Delete icons |
Creating a Group
Click + Add Group to open the creation form.
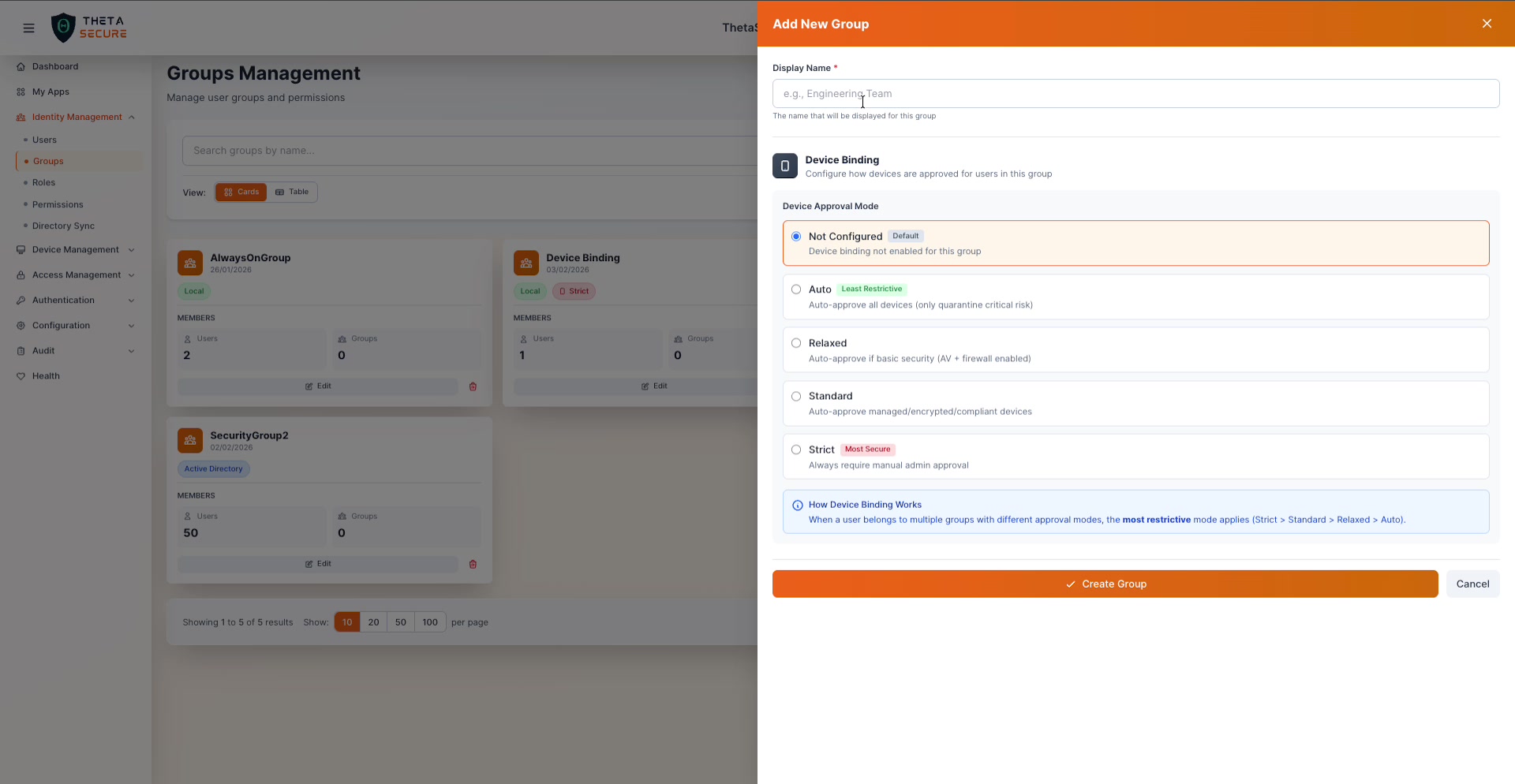
Required Field
Display Name is the only required field. Use a name that clearly identifies the group's purpose (e.g., "Engineering Team", "SOC Analysts", "VPN Users").
Device Binding
This is where groups become powerful for zero-trust security. Device Binding controls how devices are approved for users in this group. Choose one of five modes:
| Mode | Security Level | What It Does |
|---|---|---|
| Not Configured | Default | Device binding is not enabled for this group |
| Auto | Least Restrictive | Auto-approves all devices, only quarantines critical-risk devices |
| Relaxed | Low | Auto-approves devices with basic security (antivirus + firewall enabled) |
| Standard | Moderate | Auto-approves only managed, encrypted, and compliant devices |
| Strict | Most Secure | Always requires manual administrator approval for every device |
When a user belongs to multiple groups with different device approval modes, the most restrictive mode wins. The priority order is: Strict > Standard > Relaxed > Auto.
For example, if a user is in both "Engineering" (Auto) and "Privileged Access" (Strict), the Strict policy applies.
Click Create Group to save, or Cancel to discard.
Managing Group Members
Click Edit on any group card to open the member management panel.
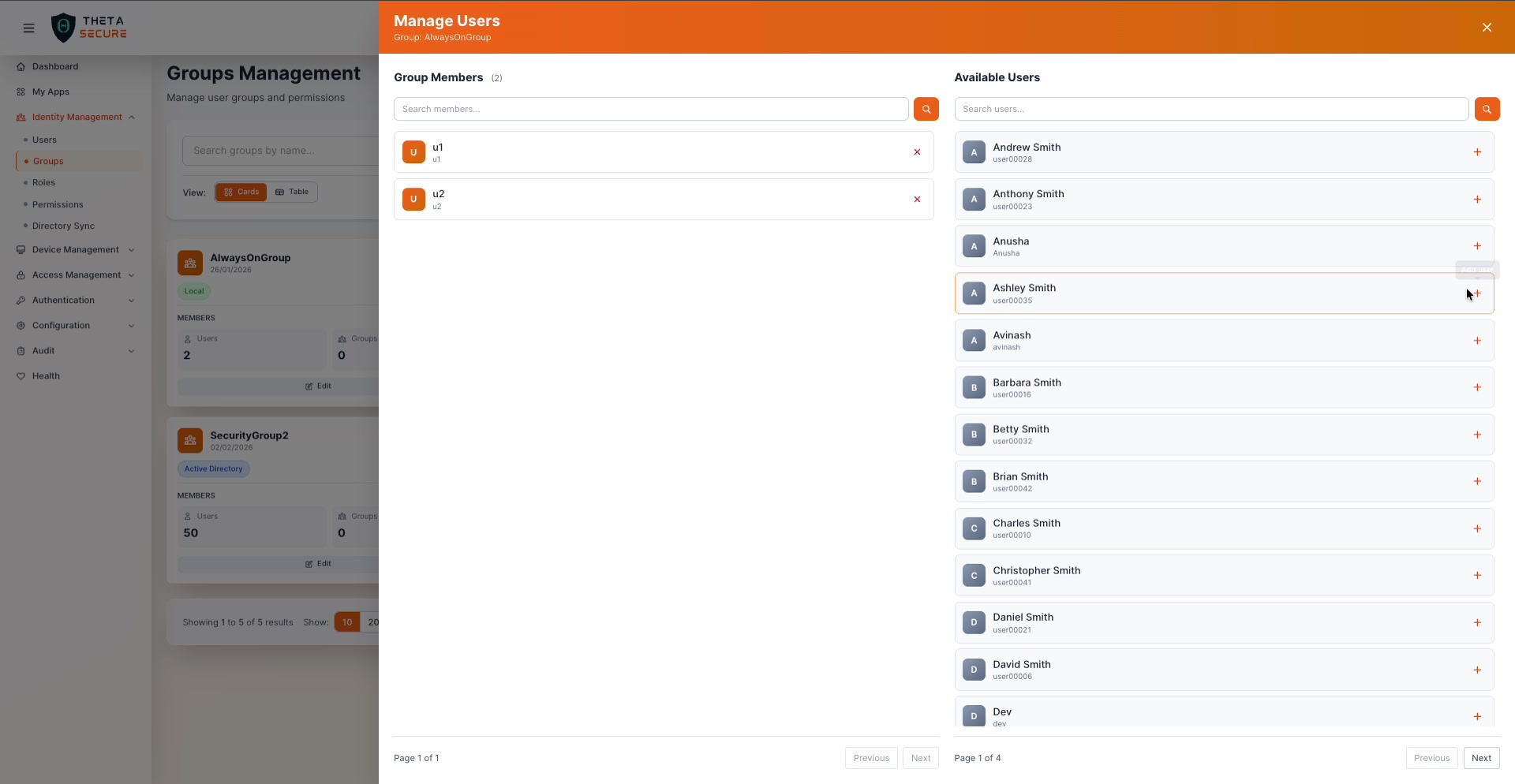
The panel is split into two columns:
Group Members (left side) shows current members of the group. Each member has an ✕ button to remove them.
Available Users (right side) lists all users not currently in the group. Click the + button next to any user to add them. Both columns are searchable, and the available users list is paginated.
Groups also support nested groups. Hover over the "Groups" count on any card to see the tooltip "Click to manage nested groups." This lets you build group hierarchies where child groups inherit the parent's access and device binding policies.
Deleting a Group
Click the delete icon (🗑) on any group card or table row. A confirmation dialog appears showing exactly how many users and nested groups will be affected:
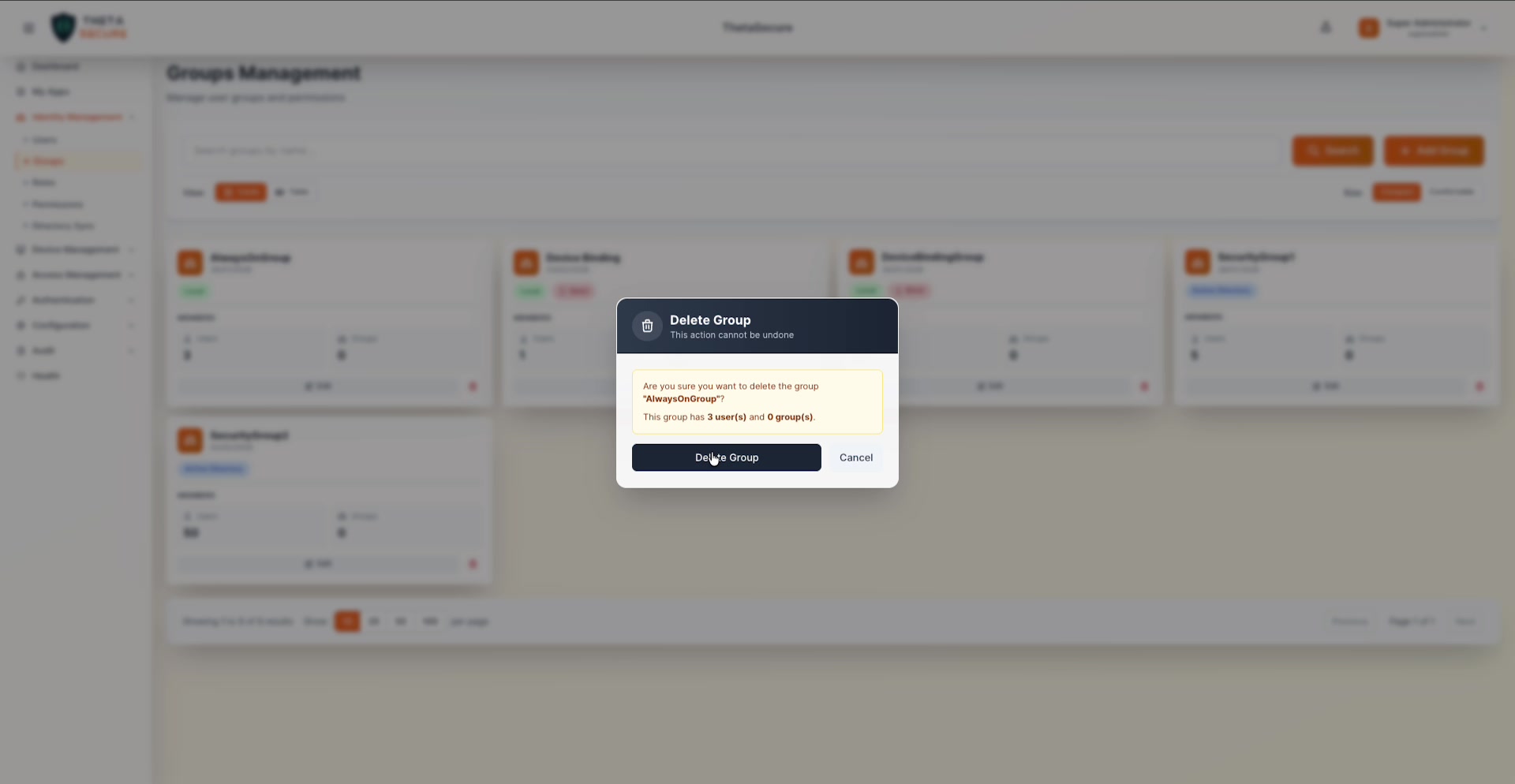
The dialog warns that this action cannot be undone and displays the impact (e.g., "This group has 3 user(s) and 0 group(s)"). Users are not deleted when a group is removed; they simply lose the access and policies that were inherited through the group.
Current Groups
Based on the current environment, ThetaSecure has 5 groups configured:
| Group | Source | Users | Device Binding |
|---|---|---|---|
| AlwaysOnGroup | Local | 3 | Not configured |
| Device Binding | Local | 1 | Strict |
| DeviceBindingGroup | Local | 1 | Strict |
| SecurityGroup1 | Active Directory | 5 | Not configured |
| SecurityGroup2 | Active Directory | 50 | Not configured |
Best Practices
Mirror your org structure. Create groups that match your departments, teams, or project units. When someone moves teams, update their group membership rather than reconfiguring individual permissions.
Use device binding on sensitive groups. For groups with access to critical infrastructure, set the device binding to Standard or Strict. This ensures only trusted, compliant devices can reach sensitive resources.
Keep directory-synced groups read-only. Groups imported from Active Directory should be managed in the source directory. Making local changes risks conflicts during the next sync cycle.
Leverage nested groups for inheritance. Instead of duplicating configurations, create a parent group with shared policies and nest team-specific groups under it.