Remote Servers
Remote Servers provide secure, browser based access to internal servers over SSH, RDP, VNC, and Telnet. This is designed for scenarios where administrators need to grant server access to third party contractors, vendors, or temporary users without installing the ThetaSecure agent on their devices and without exposing servers directly to the internet.
The user opens a browser, authenticates through ThetaSecure, and gets a fully interactive terminal (SSH/Telnet) or desktop session (RDP/VNC) rendered in the browser. ThetaSecure acts as the secure gateway between the user and the target server, enforcing session timeouts, recording sessions for compliance, and applying granular controls over what the user can do during the session, such as blocking clipboard access, file transfers, or screenshots.
This eliminates the need for traditional VPN tunnels or jump servers when providing third party access. The administrator retains full control over session duration, authentication method, and data movement, while the third party user needs nothing more than a web browser.
 The Remote Servers page in its empty state. The page includes a search bar, an All Protocols filter dropdown, an All States filter dropdown, and the "+ Add Remote Server" button. The empty state prompts: "Create your first remote access application to enable secure SSH/RDP/VNC access."
The Remote Servers page in its empty state. The page includes a search bar, an All Protocols filter dropdown, an All States filter dropdown, and the "+ Add Remote Server" button. The empty state prompts: "Create your first remote access application to enable secure SSH/RDP/VNC access."
The Remote Servers Page
The page follows the same layout as other Access Management sections: a search bar for filtering by name or description, two filter dropdowns (All Protocols and All States), and a + Add Remote Server button. Cards and Table views are available, along with Compact and Comfortable sizing options.
The All Protocols filter lets you narrow the list to show only SSH, RDP, VNC, or Telnet servers. The All States filter lets you show active, inactive, or all servers.
Creating a Remote Server
Click + Add Remote Server to open the Create Remote Server panel.
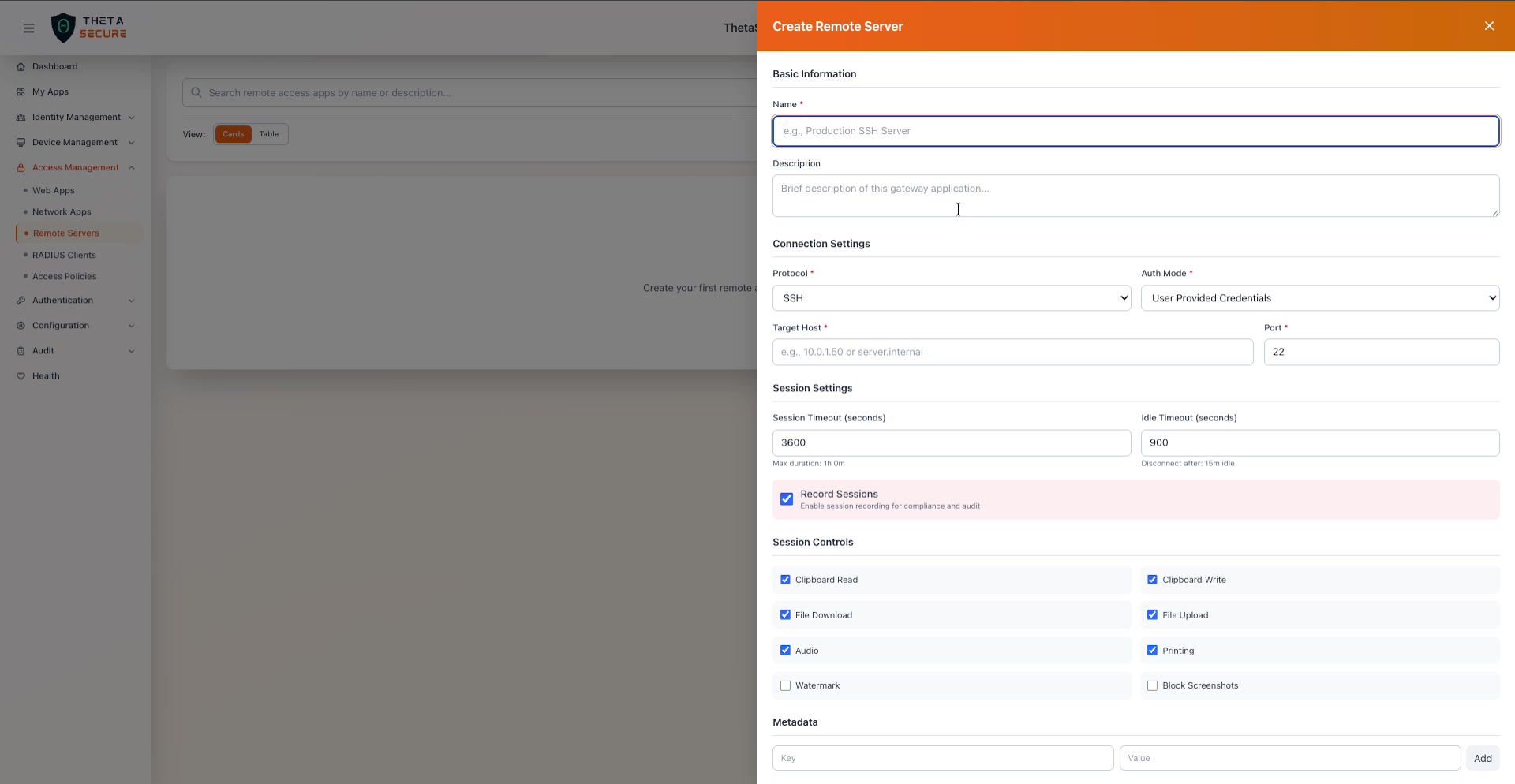 The complete Create Remote Server form. Basic Information at the top, followed by Connection Settings (Protocol, Auth Mode, Target Host, Port), Session Settings (timeouts and recording), Session Controls (eight granular checkboxes), and Metadata at the bottom.
The complete Create Remote Server form. Basic Information at the top, followed by Connection Settings (Protocol, Auth Mode, Target Host, Port), Session Settings (timeouts and recording), Session Controls (eight granular checkboxes), and Metadata at the bottom.
Basic Information
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Yes | A descriptive name for the remote server (e.g., "Production SSH Server", "Staging Windows Desktop", "Vendor Database Access"). |
| Description | No | A brief description of this gateway application and its intended audience. |
Connection Settings
Connection Settings define which server to connect to, what protocol to use, and how users authenticate to the target server.
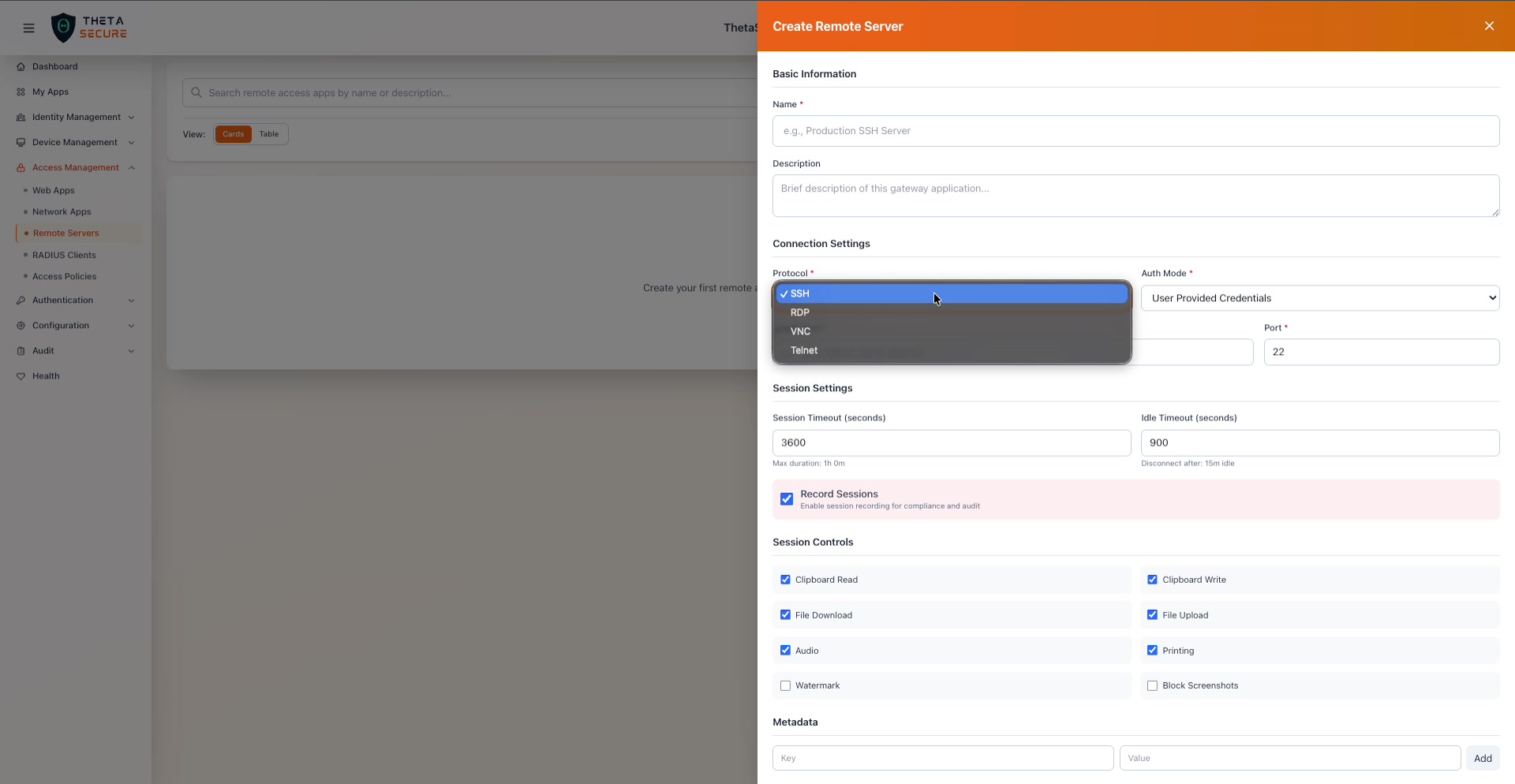 The Protocol dropdown expanded, showing all four supported protocols: SSH, RDP, VNC, and Telnet.
The Protocol dropdown expanded, showing all four supported protocols: SSH, RDP, VNC, and Telnet.
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | Yes | The remote access protocol. Four options are available: SSH for Linux/Unix command line access, RDP for Windows remote desktop sessions, VNC for cross platform graphical desktop access, and Telnet for legacy devices that require unencrypted terminal access. |
| Auth Mode | Yes | How the user authenticates to the target server. See the Auth Mode section below for details on each option. |
| Target Host | Yes | The IP address or hostname of the target server (e.g., 10.0.1.50 or server.internal). This must be reachable from the ThetaSecure gateway. |
| Port | Yes | The port number for the connection. Defaults to the standard port for the selected protocol: 22 for SSH, 3389 for RDP, 5900 for VNC, 23 for Telnet. |
Auth Mode
The Auth Mode dropdown controls how the user authenticates to the target server once ThetaSecure has established the gateway connection. This is separate from ThetaSecure authentication, which happens first. The user always authenticates to ThetaSecure through SSO/MFA before reaching the server.
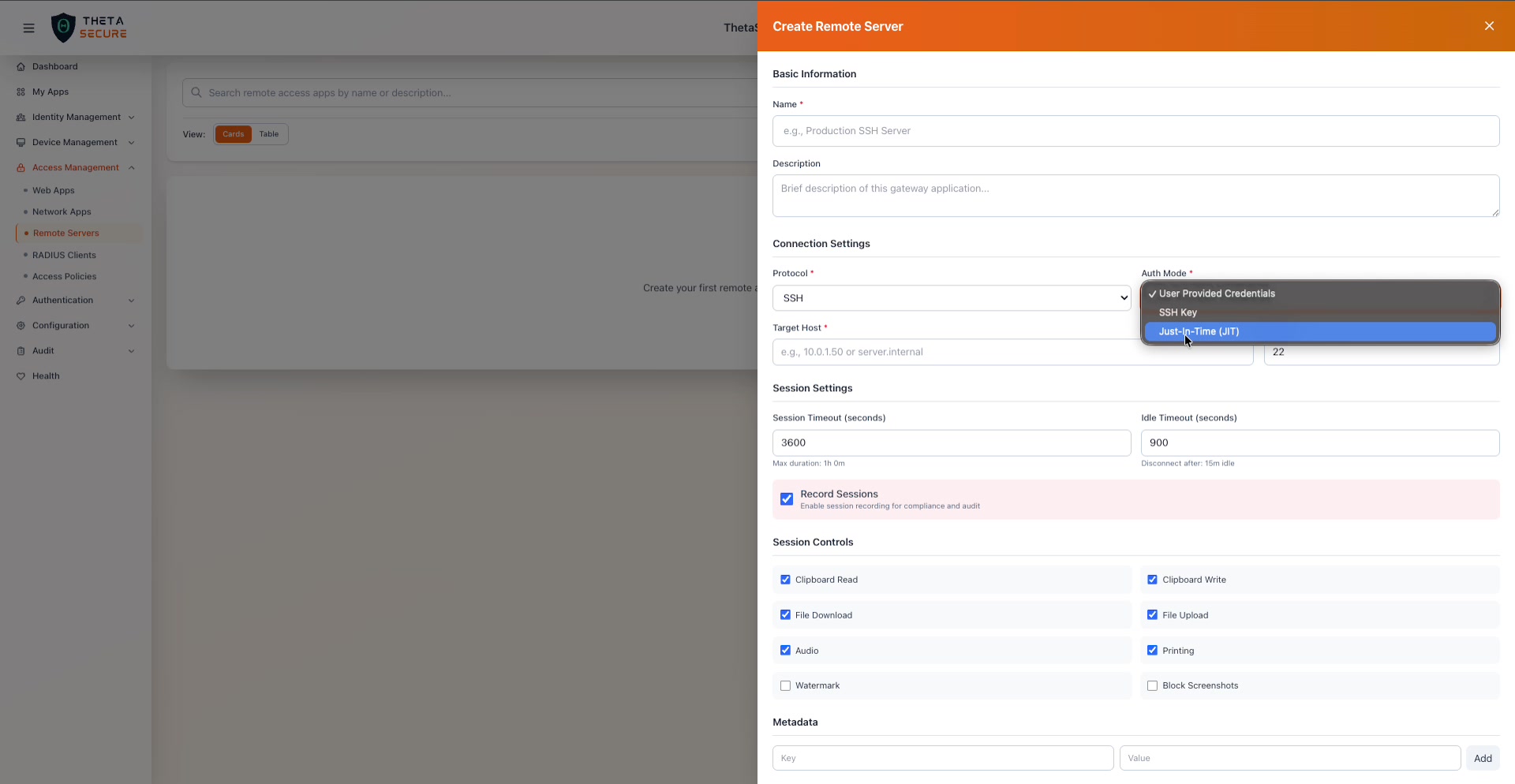 The Auth Mode dropdown showing all three options: User Provided Credentials, SSH Key, and Just-In-Time (JIT).
The Auth Mode dropdown showing all three options: User Provided Credentials, SSH Key, and Just-In-Time (JIT).
| Auth Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| User Provided Credentials | The user enters their own username and password when the session starts. ThetaSecure passes these credentials to the target server. This is the simplest option and works when users already have server accounts. |
| SSH Key | ThetaSecure uses a pre-configured SSH key pair to authenticate to the target server. The user does not need to know or provide server credentials. This is the most secure option for SSH connections because credentials are never exposed to the user. |
| Just-In-Time (JIT) | ThetaSecure dynamically provisions a temporary account on the target server for the duration of the session. When the session ends, the account is removed. This is the most secure option for third party access because no standing credentials exist on the server. The contractor or vendor gets access only for the duration of their session, with no persistent account left behind. |
For third party and vendor access, Just-In-Time (JIT) is the recommended Auth Mode. It eliminates the risk of standing credentials on target servers. The temporary account exists only for the session duration and is automatically cleaned up when the session ends or times out.
Session Settings
Session Settings control how long sessions can last and whether they are recorded.
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Session Timeout (seconds) | 3600 (1 hour) | The maximum duration of a single session. After this time, the session is automatically terminated regardless of activity. The helper text below the field shows the human readable duration (e.g., "Max duration: 1h 0m"). |
| Idle Timeout (seconds) | 900 (15 minutes) | How long a session can remain idle before it is automatically disconnected. The helper text reads "Disconnect after: 15m idle". |
| Record Sessions | Enabled | When enabled, ThetaSecure records the full session for compliance and audit purposes. Session recordings capture every keystroke (SSH/Telnet) or screen interaction (RDP/VNC) and can be reviewed later by administrators. This is critical for third party access where organizations need an audit trail of exactly what a vendor or contractor did on the server. |
Session Controls
Session Controls provide granular restrictions on what users can do during a remote session. These are especially important for third party access, where you want to prevent data exfiltration or unauthorized actions.
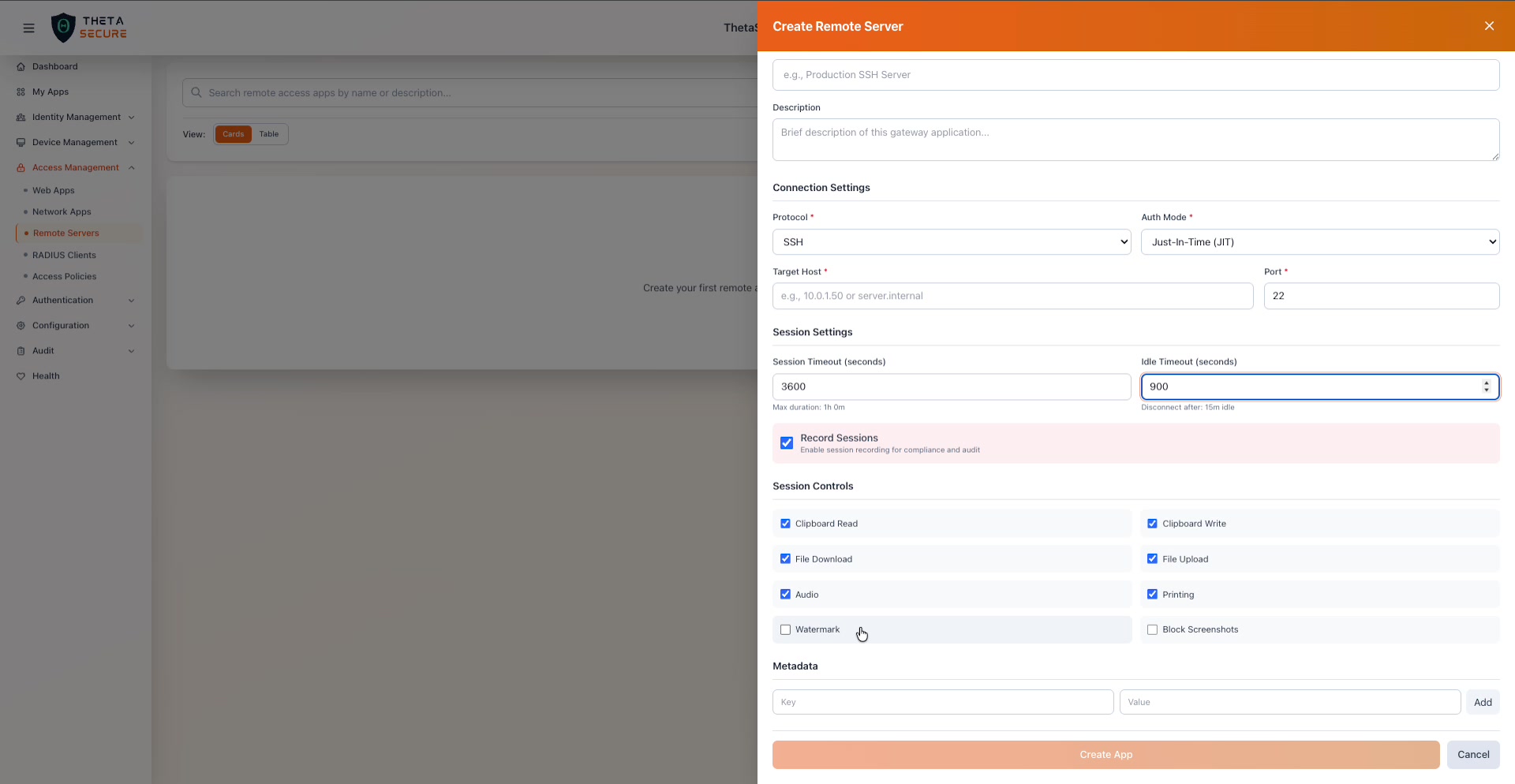 Session Controls with six options enabled by default (Clipboard Read, Clipboard Write, File Download, File Upload, Audio, Printing) and two disabled by default (Watermark, Block Screenshots). The Metadata section and Create App button are visible below.
Session Controls with six options enabled by default (Clipboard Read, Clipboard Write, File Download, File Upload, Audio, Printing) and two disabled by default (Watermark, Block Screenshots). The Metadata section and Create App button are visible below.
| Control | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Clipboard Read | Enabled | Allows the user to paste content from the remote session into their local clipboard. Disable this to prevent users from copying sensitive data out of the session. |
| Clipboard Write | Enabled | Allows the user to paste content from their local clipboard into the remote session. Disable this if you want to prevent users from injecting commands or data into the server. |
| File Download | Enabled | Allows the user to download files from the remote server to their local machine. Disable this to prevent data exfiltration. |
| File Upload | Enabled | Allows the user to upload files from their local machine to the remote server. Disable this to prevent unauthorized file transfers. |
| Audio | Enabled | Allows audio streaming from the remote session (relevant for RDP and VNC). |
| Printing | Enabled | Allows the user to print from within the remote session. |
| Watermark | Disabled | When enabled, overlays a visible watermark on the session screen. The watermark typically includes the user's identity and timestamp, which deters photography of the screen and helps trace the source of any leaked screenshots. |
| Block Screenshots | Disabled | When enabled, prevents screenshot capture during the session. This adds a technical barrier to screen capture beyond the visual deterrent of watermarking. |
For high security third party access, consider disabling Clipboard Read, File Download, and File Upload to prevent data exfiltration. Enable Watermark and Block Screenshots to deter and block screen capture. Combined with session recording, this creates a comprehensive security posture where the third party can perform their work but cannot extract sensitive data.
Metadata
Metadata provides the same flexible key value store as Network Apps. Use it for tagging servers with environment names, ownership, compliance requirements, or any other organizational data.
Creating the Server
Click Create App to register the remote server. Once created, the server appears as a card on the Remote Servers page. Users who are granted access through access policies will see the server in their ThetaSecure portal and can launch a browser based session directly.
When to Use Remote Servers vs. Network Apps
Remote Servers and Network Apps both provide access to internal resources, but they serve different use cases.
Use Remote Servers when you need to provide interactive terminal or desktop access to specific servers, especially for third party users who do not have the ThetaSecure agent installed. The browser based session means the user needs nothing on their device other than a web browser. Session recording, clipboard controls, and file transfer restrictions provide the security controls that third party access demands.
Use Network Apps when users need network level access to internal resources through the ThetaSecure agent. Network Apps are for your own employees and managed devices, where the agent creates an encrypted micro-tunnel to specific IP/port combinations. Network Apps do not provide interactive sessions; they provide network connectivity so the user's own applications (SSH clients, database tools, web browsers) can reach internal resources.
In some environments, you may use both. An employee with a managed device would use Network Apps to reach internal servers through their preferred SSH client. A third party contractor without the agent would use Remote Servers to access the same server through the browser, with session recording enabled and clipboard access disabled.