SignIn Policies
SignIn policies are the top-level configuration that brings together your authentication profiles and MFA profiles into enforceable access rules. Each policy defines which sign-in profile handles primary authentication, which MFA profile provides second-factor verification, and under what conditions these apply. Policies are evaluated by priority when a user attempts to sign in, and the first matching policy determines the authentication flow.
ThetaSecure includes a Default Sign-In Policy that applies to all users as a baseline. You can create additional policies with higher priorities to override the default for specific user populations, network ranges, or security contexts.
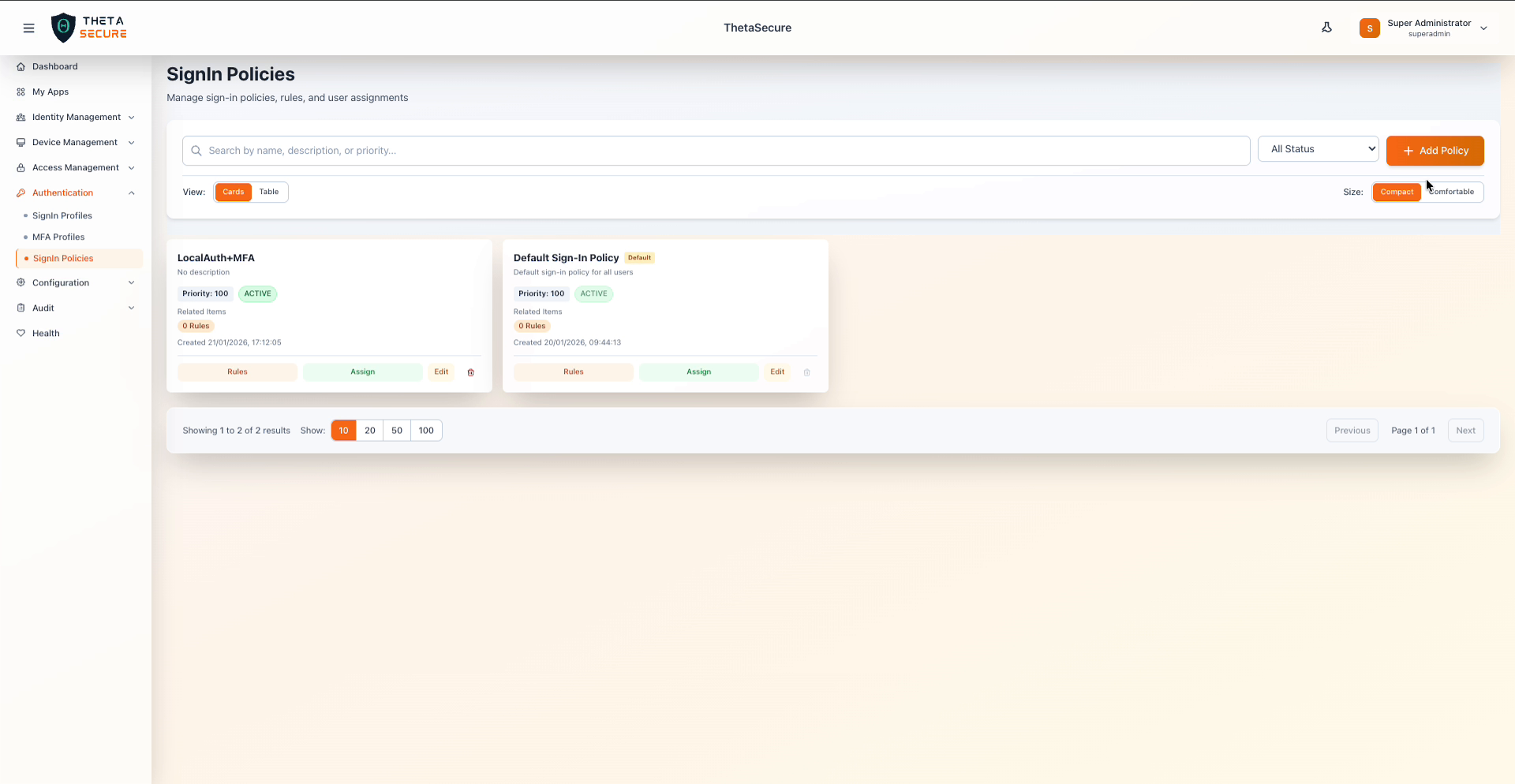 The SignIn Policies page showing two policies with their priority, status, rule counts, and action buttons for Rules, Assign, and Edit.
The SignIn Policies page showing two policies with their priority, status, rule counts, and action buttons for Rules, Assign, and Edit.
Creating a SignIn Policy
Navigate to Authentication > SignIn Policies and click + Add Policy. The creation form collects the policy name, description, and priority.
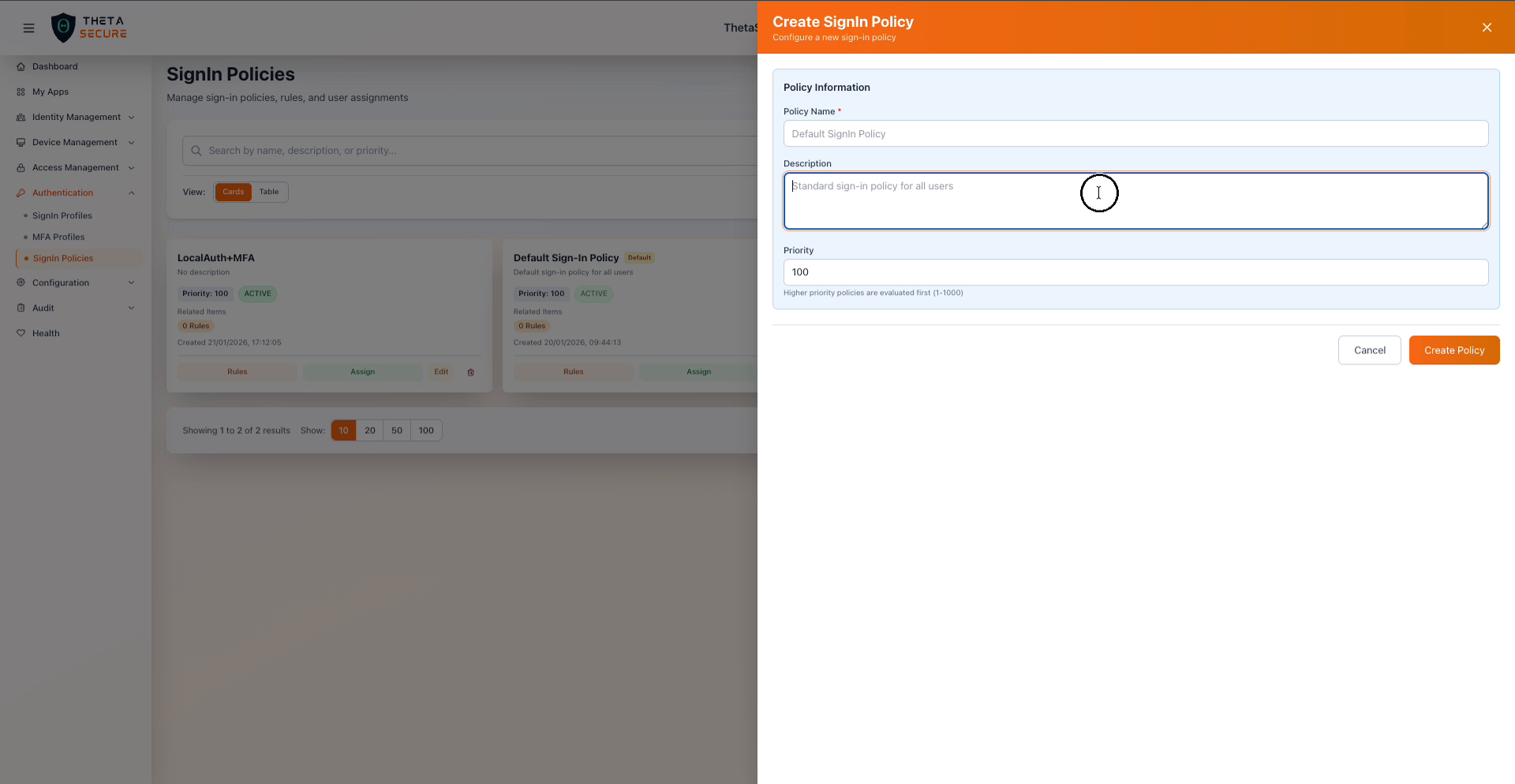 The Create SignIn Policy form showing the Policy Information section.
The Create SignIn Policy form showing the Policy Information section.
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Policy Name | Yes | A descriptive name that indicates the policy's purpose, such as "Corporate Network Auth" or "Contractor MFA Required". |
| Description | No | An optional explanation of what this policy does and who it targets. |
| Priority | Yes | A numeric value between 1 and 1000. Higher priority policies are evaluated first. |
After creating the policy, configure it by adding rules and assigning it to users or groups.
Policy Rules
Rules within a sign-in policy define the actual authentication behavior. Each rule specifies the conditions under which it applies and the actions to take when those conditions are met. To manage rules, click the Rules button on the policy card.
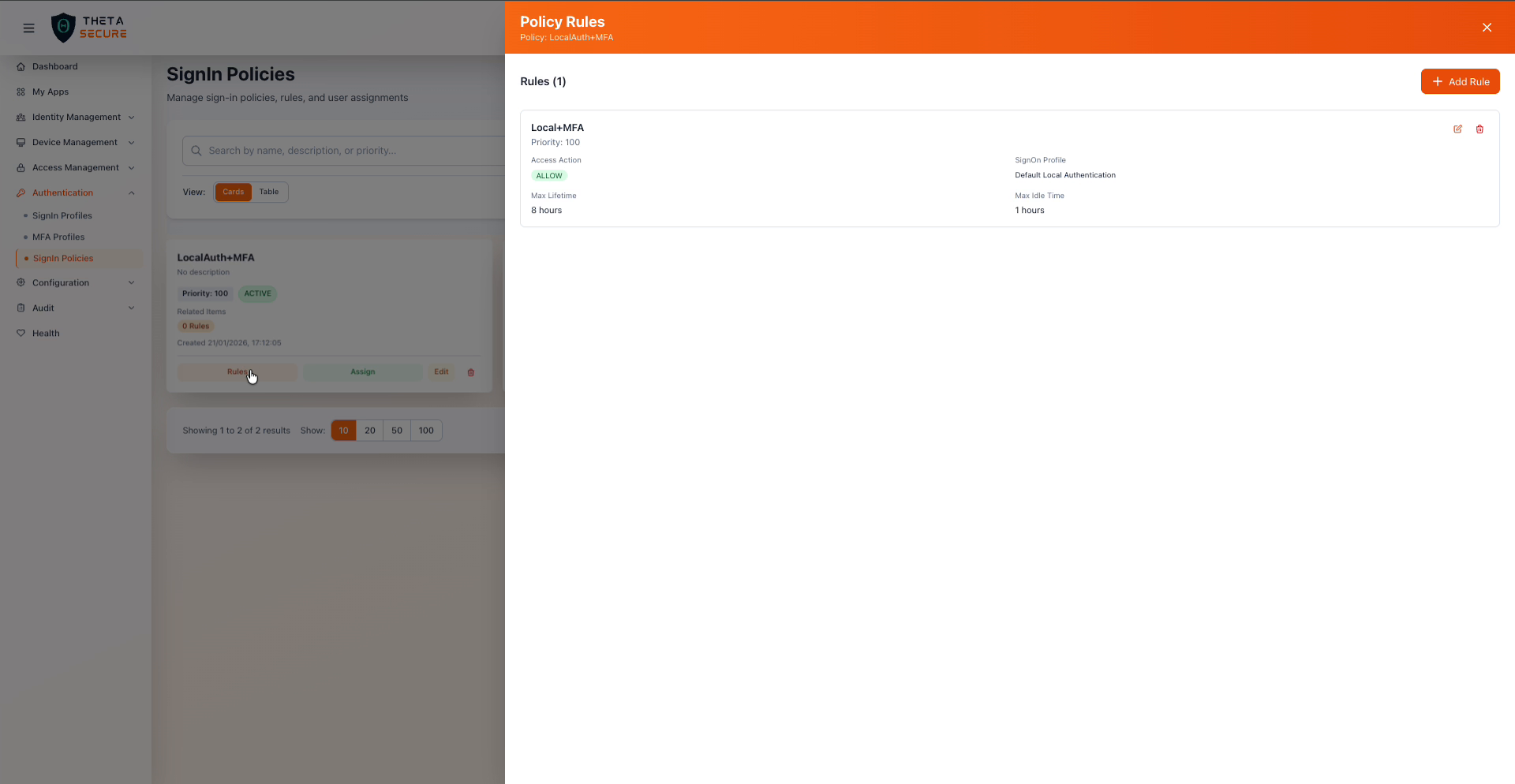 The Policy Rules panel for the LocalAuth+MFA policy showing one configured rule with its access action, sign-on profile, and session settings.
The Policy Rules panel for the LocalAuth+MFA policy showing one configured rule with its access action, sign-on profile, and session settings.
Adding a Rule
Click + Add Rule to expand the rule creation form.
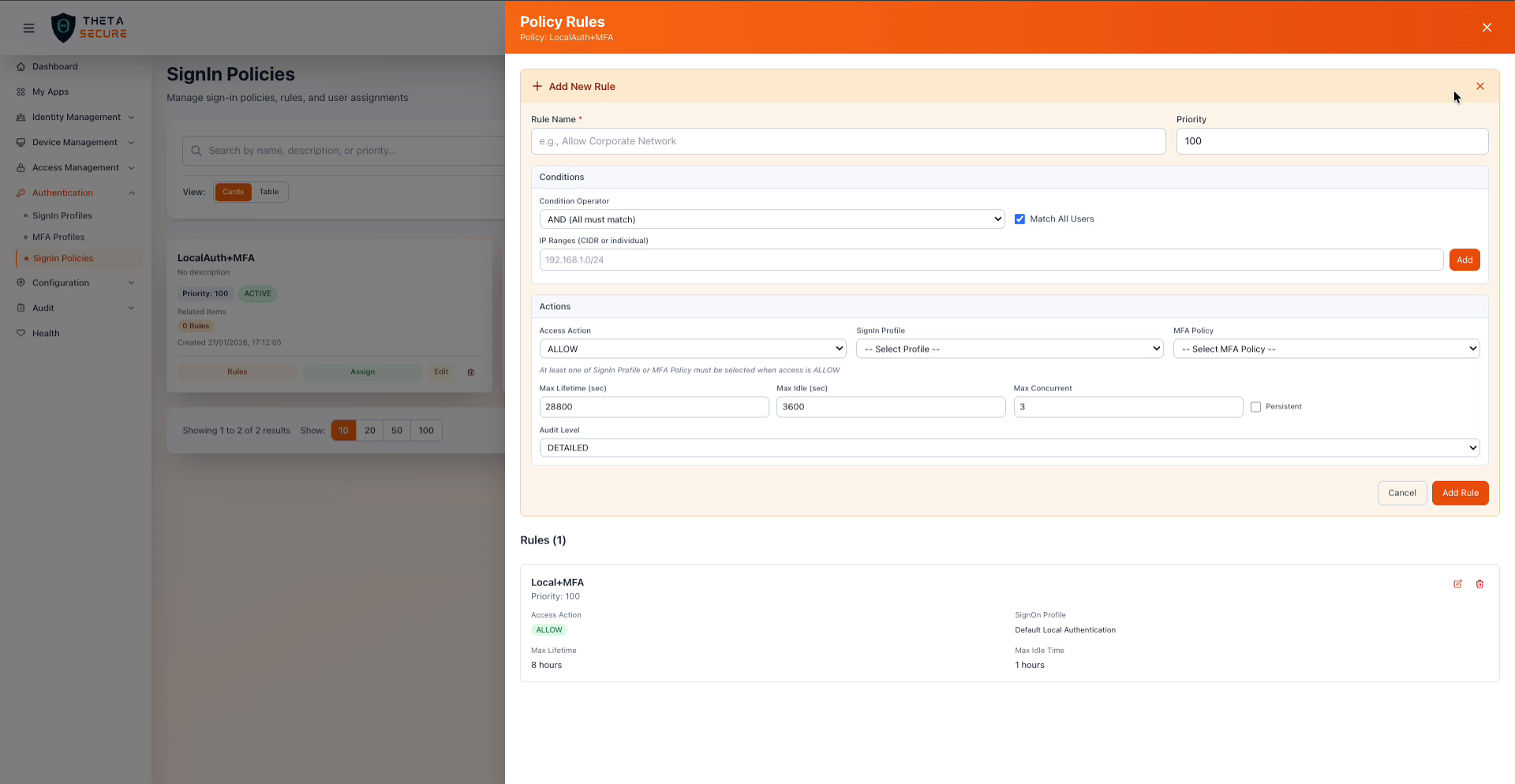 The Add New Rule form showing all configurable fields including conditions, actions, and session parameters.
The Add New Rule form showing all configurable fields including conditions, actions, and session parameters.
Rule Name and Priority
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Rule Name | Yes | A descriptive name such as "Allow Corporate Network" or "Block External After Hours". |
| Priority | Yes | Controls evaluation order within this policy. Default is 100. |
Conditions
Conditions determine which authentication attempts this rule applies to.
| Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| Condition Operator | Controls how multiple conditions are combined. AND (All must match) requires every condition to be true. |
| Match All Users | When checked, the rule applies to every user. Uncheck to target specific user populations. |
| IP Ranges (CIDR or individual) | Restrict the rule to authentication attempts from specific IP addresses or CIDR blocks. Enter an IP range and click Add to include it. |
Actions
The Actions section defines what happens when the rule's conditions are met.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Access Action | Set to ALLOW to permit authentication under this rule's conditions. |
| SignIn Profile | The authentication profile used for primary authentication. Select from your configured sign-in profiles. At least one of SignIn Profile or MFA Policy must be selected when the access action is ALLOW. |
| MFA Policy | The MFA profile that provides second-factor requirements. Select from your configured MFA profiles. |
 The SignIn Profile dropdown populated with the authentication profiles configured in your environment.
The SignIn Profile dropdown populated with the authentication profiles configured in your environment.
You can assign both a SignIn Profile and an MFA Policy to a single rule. This creates a complete authentication flow where the user first authenticates with their primary credentials (local or AD) and then completes a second-factor challenge based on the MFA profile's rules.
Session Parameters
Session parameters control the authenticated session behavior after a user successfully signs in.
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Max Lifetime (sec) | 28800 | The maximum duration of a session in seconds, regardless of activity. 28800 seconds equals 8 hours, which covers a standard workday. |
| Max Idle (sec) | 3600 | The maximum time a session can remain inactive before requiring re-authentication. 3600 seconds equals 1 hour. |
| Max Concurrent | 3 | The maximum number of simultaneous active sessions allowed for a single user. |
| Persistent | Off | When enabled, sessions survive browser restarts. Leave disabled for environments where users should re-authenticate when they close and reopen their browser. |
| Audit Level | DETAILED | The level of detail captured in authentication audit logs. DETAILED records comprehensive information about each sign-in attempt. |
Policy Assignments
Click the Assign button on a policy card to manage which users and groups are covered by the policy. The assignment determines the scope of the policy's rules. Users who are not assigned to any custom policy fall through to the Default Sign-In Policy.
Policy Card Actions
Each policy card displays the policy name, description, status, priority, and related items summary. The available actions are:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Rules | Open the Policy Rules panel to manage authentication rules |
| Assign | Open the assignment panel to manage user and group assignments |
| Edit | Modify the policy name, description, or priority |
| Delete | Permanently remove the policy (not available for the Default Sign-In Policy) |
Policy Evaluation
When a user attempts to sign in, ThetaSecure evaluates all active sign-in policies in priority order. The evaluation follows this flow:
The system checks each policy starting with the highest priority. For each policy, it verifies whether the user is assigned to that policy (directly or through a group). If the user matches, the system evaluates the policy's rules in their own priority order. The first rule whose conditions match the authentication attempt determines the authentication flow, including which sign-in profile and MFA policy to apply, and how to configure the resulting session.
If no custom policy matches, the Default Sign-In Policy serves as the catch-all.
Best Practices
Layer policies by security sensitivity. Create a high priority policy for administrators that requires AD authentication plus hardware key MFA, a medium priority policy for standard employees with local authentication plus TOTP, and leave the Default Sign-In Policy as a restrictive fallback that denies access or requires the strictest MFA.
Use IP range conditions to differentiate corporate and remote access. A common pattern is to create two rules within a policy: one that matches your corporate network CIDR ranges with relaxed MFA requirements, and another that catches all other IP addresses with mandatory MFA on every login. This reduces friction for users inside the office while maintaining security for remote access.
Set session lifetimes based on the sensitivity of accessible resources. For policies covering high security applications, reduce Max Lifetime to 4 hours (14400 seconds) and Max Idle to 15 minutes (900 seconds). For general productivity applications, the defaults of 8 hours and 1 hour provide a reasonable balance between security and usability.
Keep Max Concurrent sessions low for privileged accounts. Limiting administrators to one or two concurrent sessions helps detect credential sharing and reduces the window of exposure if a session token is compromised. Standard users can safely have three to five concurrent sessions to accommodate multiple browser tabs or devices.
Audit your policy assignments regularly. Review which users and groups are assigned to each policy to ensure the mappings still reflect your organizational structure. Employees who change roles may need to move between policies, and departing users should be removed from all custom policy assignments.